- TPM definition
- TPM Philosophy
- TPM Essence
- Improvement lead to real benefits
- Case of small amount of work
- TPM organization
- TPM History
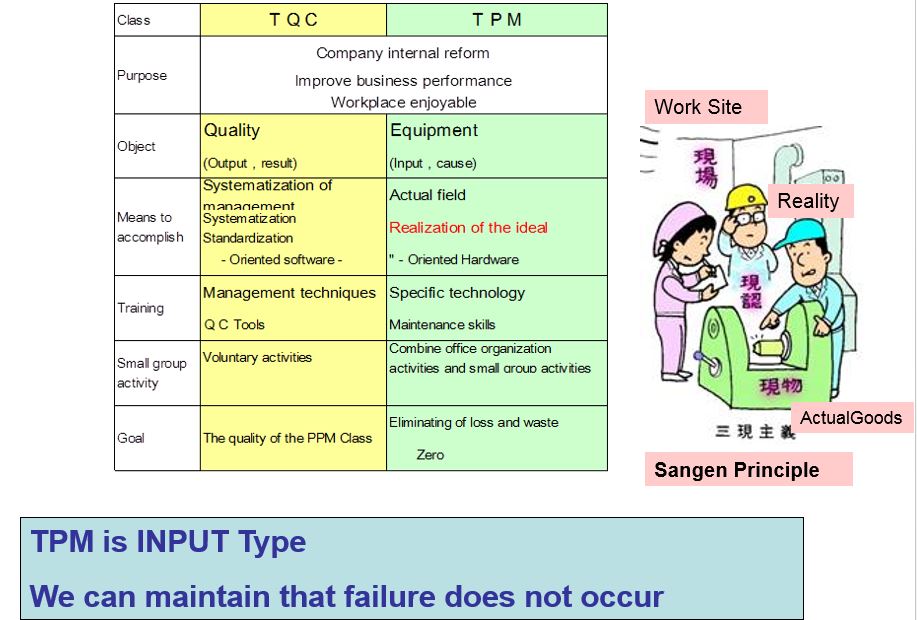
- TQC and TPM
- Step 12 of The TPM program
- 8 main pillars of TPM
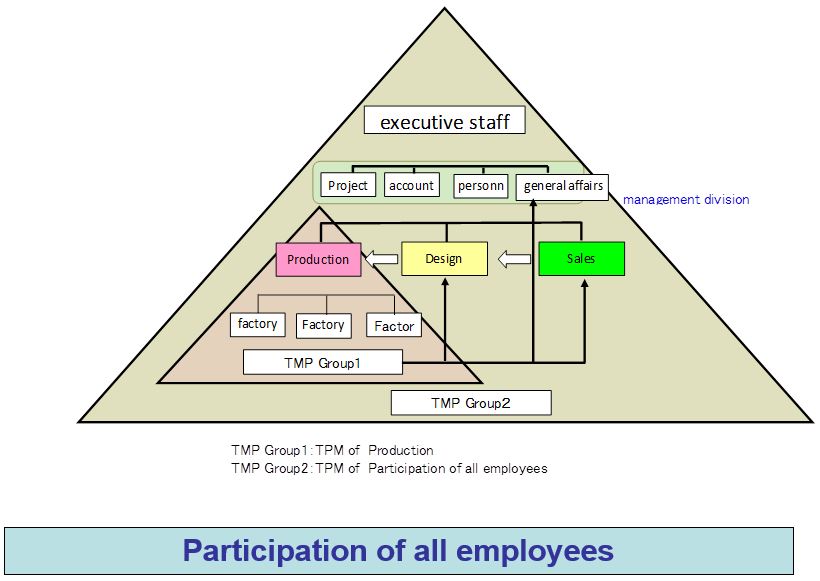
- Participation of all employees
- TPM Promotion Organization
- Case of TPM Promotion organization
- TPM basic policy and Goal
- Share SlideShare
TPM definition
・ Establishing a corporate culture that will maximize production
system effectiveness,
・ Organizing a practical shop-floor system to prevent losses before they occur throughout the entire production system life cycle, with aview to achieving zero accidents, zero defects and zero breakdowns,
・Involving all the functions of an organization including production,development, sales and management
・ Involving every employee, from top management down to front-line operators, and
・ Achieving zero losses through the activities of “overlapping small groups.
TPM Philosophy
QC:Activities to reduce the loss
→can not be zero
Waiting activities ・・・
From the occurrence of failure then analysis, measures,improvement.
TPM:Activities to prevent loss
Activity before the occurrence of the failure
→can be a zero.
Proactive improvement activities ・・・ Analysis before failure occurs, measures, improvement
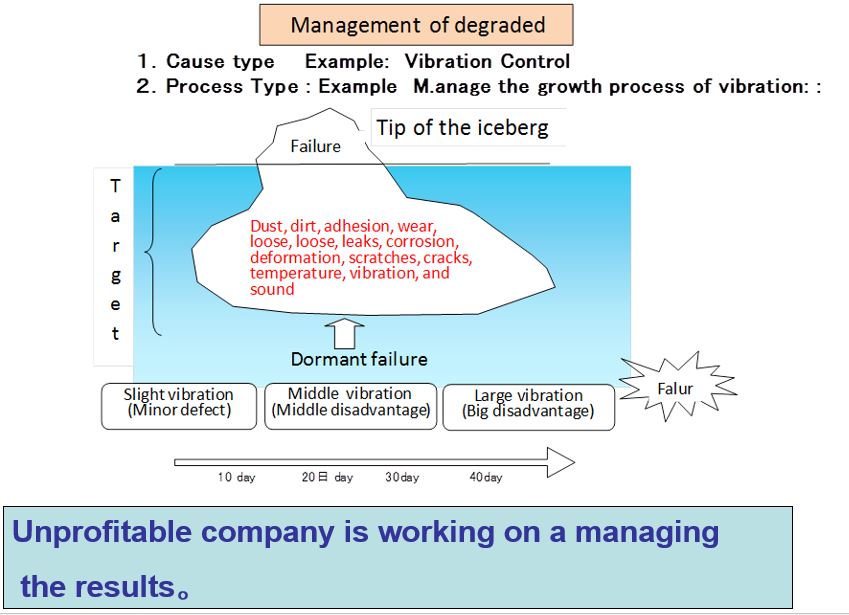
TPM Essence
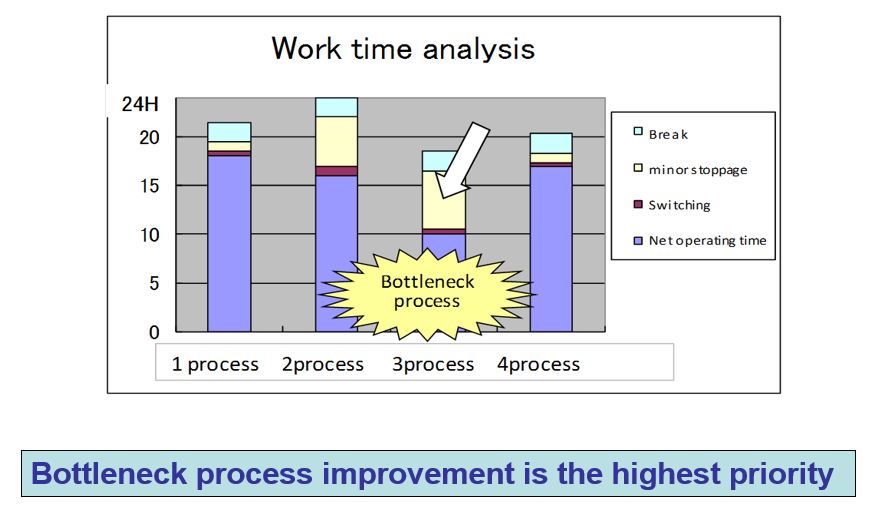
Improvement lead to real benefits
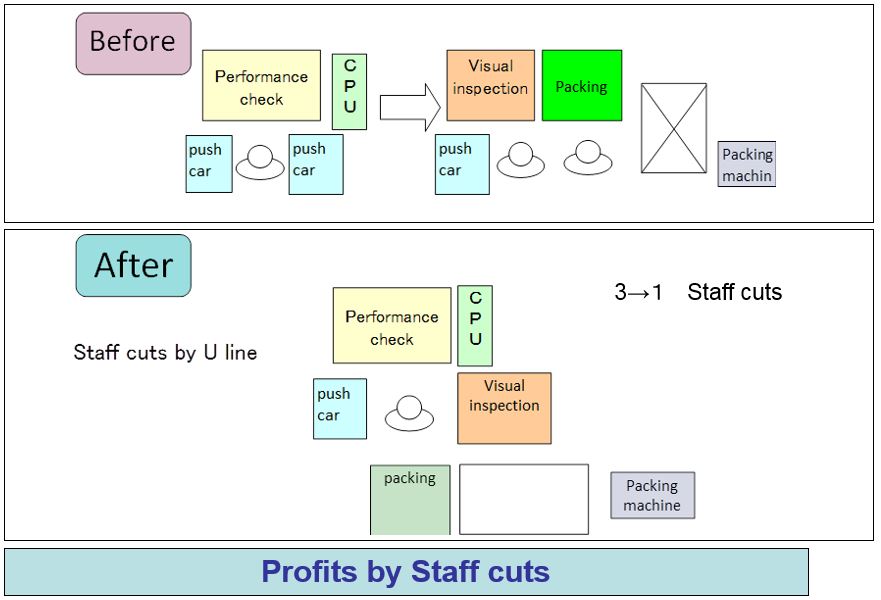
Case of small amount of work
TPM organization
TPM History
The TPM’s definition was established in 1971 as TPM was first introduced
in industry. The initial emphasis of TPM was primarily on the production
floor, but as the focus shifted to the company-wide implementation, a new
TPM definition was introduced in 1989. While the new definition
emphasizes “company-wide TPM,” the old definition focused on “TPM for
the production sector.
TPM stands for total productive maintenance. It was first advocated by the
Japan Institute of Plant Engineering (JIPE), the forerunner of the present
Japan Institute oi Plant Maintenance (JIPM). TPM has been developed
into the overall, total-company plant maintenance, unique to Japan, based
on productive maintenance (PM), introduced from the U.S.
At the initial stage of TPM advocacy, TPM centered on the production
sector.
TQC and TPM
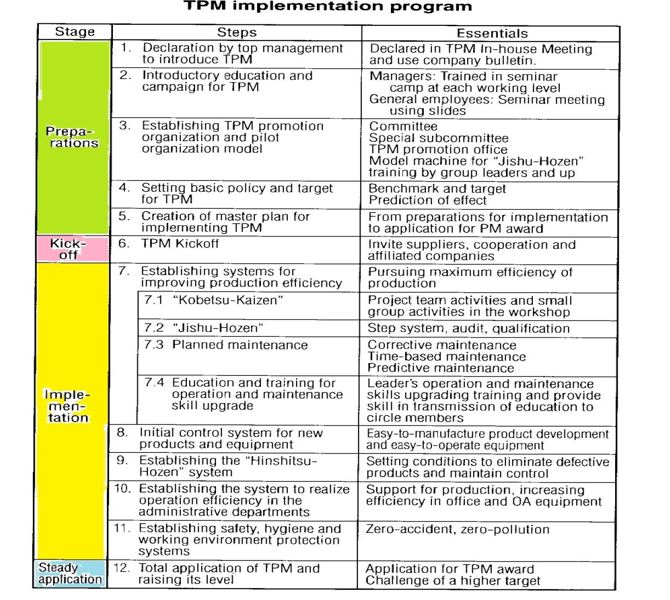
Step 12 of The TPM program
TPM is implemented through 12 steps, and these programs are called “TPM implementation program.“ The TPM implementation program can
be divided as follows:
– Preparatory stage for introduction — Steps l to 5
– introduction stage —— Step 6: Kickoff ot TPM
– Execution stage — Steps 7 to 11
– Penetration stage —— Step 12
The period for the preparatory stage for introduction varies in accordance
with the corporate scale, but generally it is executed for about six months,
by providing introductory training and setting targets thoroughly.
Subsequently, a kickoff meeting —— Step 6 ~ is held on a big scale.
The execution stage addresses the execution of the “eight pillars for of
TPM implementation.”
At the penetration stage, “TPM award” screening is applied. Generally,
about three years elapse between the kickoff and the undergoing of “TPM
award examination.”
8 main pillars of TPM
Participation of all employees
TPM Promotion Organization
Case of TPM Promotion organization
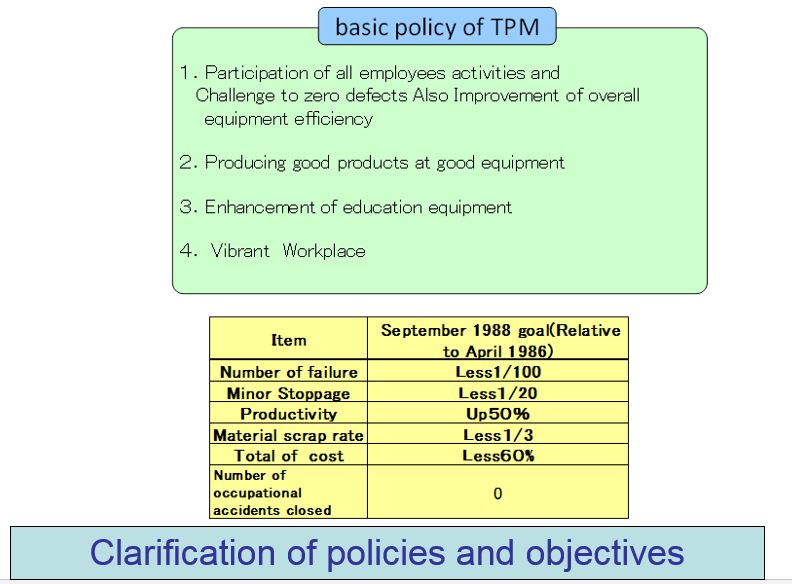
TPM basic policy and Goal
Quote From :TPM Deployment program
TPM encyclopedia Keyword Book
(Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance)
Share SlideShare
TPM for lean manufacturing | lean tools