What is Quality Control?
Definitions
The totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied need.
Quality is the ongoing process of building and sustaining relationships by assessing, anticipating, and fulfilling stated and implied need.
degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements. (as per ISO 9000:2005)
Quality from different point of views:
From customer point of view: quality means fitness for use and meeting customer satisfaction.

From process point of view: quality means conformance with the process design, standards and specifications.

From product point of view: quality means the degree of excellence at an acceptable price.

From the cost point of view: quality means best combination between costs and features.
Various Informal Definitions
Excellence
Adding value
Satisfaction
Conformance to customer needs
Attributes most important to the customer
Error-free output
Meeting Legal, Regulatory & Customer Requirements.
Usability
Value-added care and service
The maximum Variation we can get away with
Doing the things right the first time and every time
Bringing the perfectness in the system from all respects to give the optimum solution
If the criteria meets the bench mark criteria
Reduction of variation around the ‘Mean’.
State of Mind
Commitment to improve
Understanding and optimizing the whole system
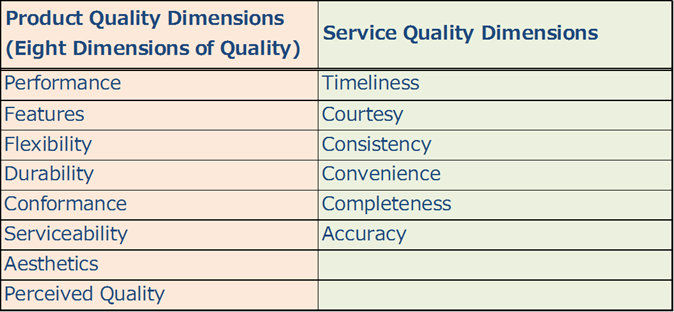
Dimensions of Quality
Three key elements of quality:
Elements which influence a product or service’s ability to satisfy customer needs :
Quality of Design : A product needs to be designed to satisfy customer needs.
Quality of Conformance : Closeness with which the finished product or supplied service matches the specifications of the original design.
Quality of Reliability : ability of the finished product to provide trouble free performance in the field, over an acceptable time period.
What is meanings of Quality Control?
Quality control is a process that is used to ensure a certain level of quality in a product or service. It might include whatever actions a business deems necessary to provide for the control and verification of certain characteristics of a product or service. Most often, it involves thoroughly examining and testing the quality of products or the results of services. The basic goal of this process is to ensure that the products or services that are provided meet specific requirements and characteristics, such as being dependable, satisfactory, safe and fiscally sound.
Companies that engage in quality control typically have a team of workers who focus on testing a certain number of products or observing services being done. The products or services that are examined usually are chosen at random. The goal of the quality control team is to identify products or services that do not meet a company’s specified standards of quality. If a problem is identified, the job of a quality control team or professional might involve stopping production or service until the problem has been corrected. Depending on the particular service or product as well as the type of problem identified, production or services might not cease entirely.
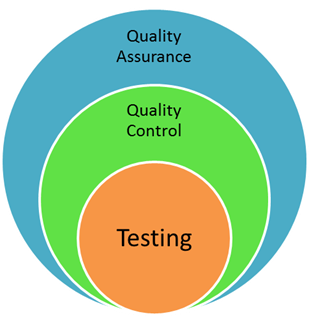
What Is The Difference Between Quality Assurance, Quality Control, And Testing?
Many people and organizations are confused about the difference between quality assurance (QA), quality control (QC), and testing. They are closely related, but they are different concepts. Since all three are necessary to effectively manage the risks of developing and maintaining software, it is important for software managers to understand the differences. They are defined below:
Quality Assurance: A set of activities designed to ensure that the development and/or maintenance process is adequate to ensure a system will meet its objectives.
Quality Control: A set of activities designed to evaluate a developed work product.
Testing: The process of executing a system with the intent of finding defects. (Note that the “process of executing a system” includes test planning prior to the execution of the test cases.)
QA activities ensure that the process is defined and appropriate. Methodology and standards development are examples of QA activities. A QA review would focus on the process elements of a project – e.g., are requirements being defined at the proper level of detail. In contrast, QC activities focus on finding defects in specific deliverables – e.g., are the defined requirements the right requirements. Testing is one example of a QC activity, but there are others such as inspections. Both QA and QC activities are generally required for successful software development.
Controversy can arise around who should be responsible for QA and QC activities — i.e., whether a group external to the project management structure should have responsibility for either QA or QC. The correct answer will vary depending on the situation, but Mosaic’s experience suggests that:
While line management should have the primary responsibility for implementing the appropriate QA, QC and testing activities on a project, an external QA function can provide valuable expertise and perspective.
The amount of external QA/QC should be a function of the project risk and the process maturity of an organization. As organizations mature, management and staff will implement the proper QA and QC approaches as a matter of habit. When this happens only minimal external guidance and review are needed.